Secondary Prevention of Cervical Cancer
Mosaic
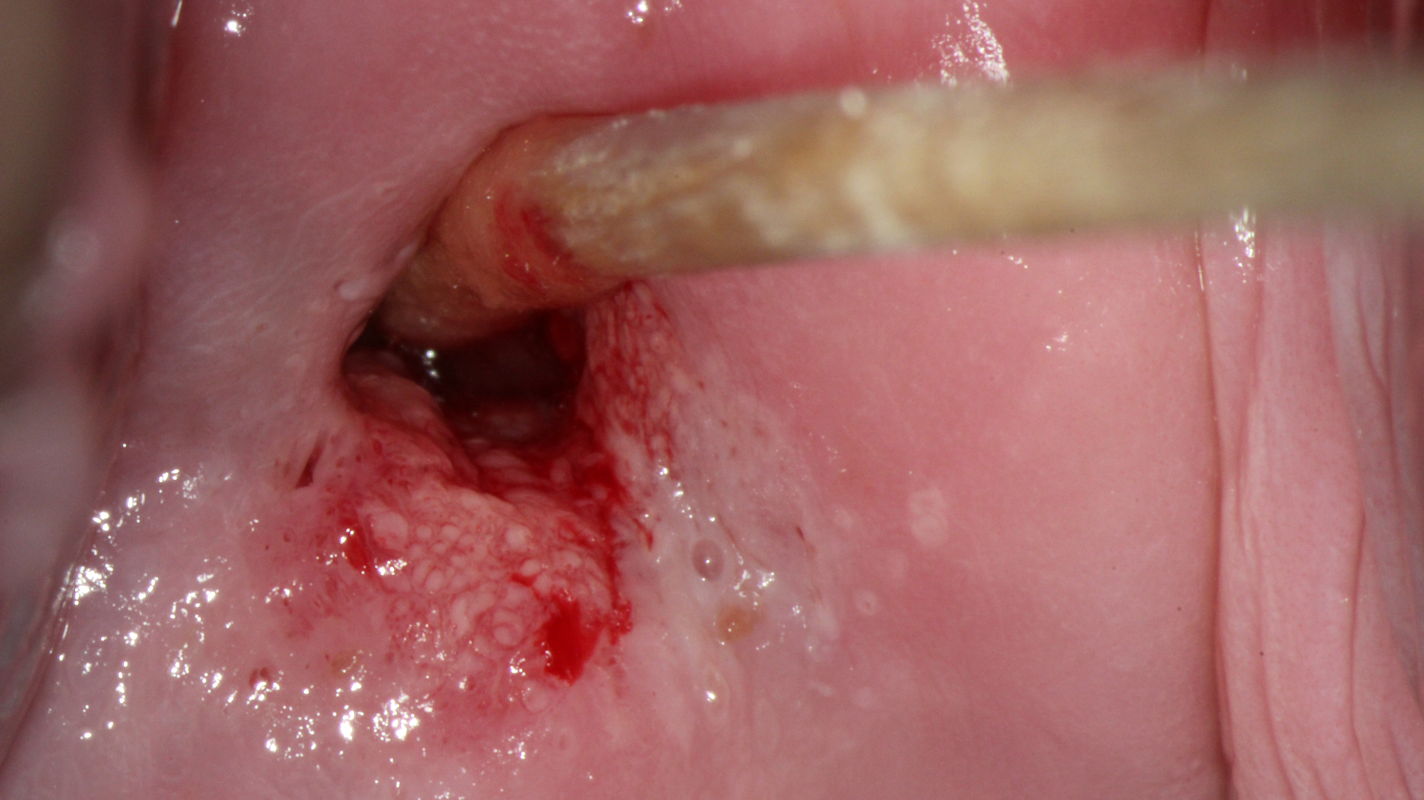
Mosaic denotes a pattern of intersecting red ridges in acetowhite epithelium.
Colposcopic findings in a 30-year-old gravida 0 with no prior history of disease. The smear was reported as class IIID1, and high risk HPV DNA and RNA were detected. Colposcopy shows an acetowhite lesion with a coarse mosaic pattern between 3 and 8 o’clock in an atypical T-zone type 2, which is classified as grade 2 (major change) abnormal colposcopic finding.
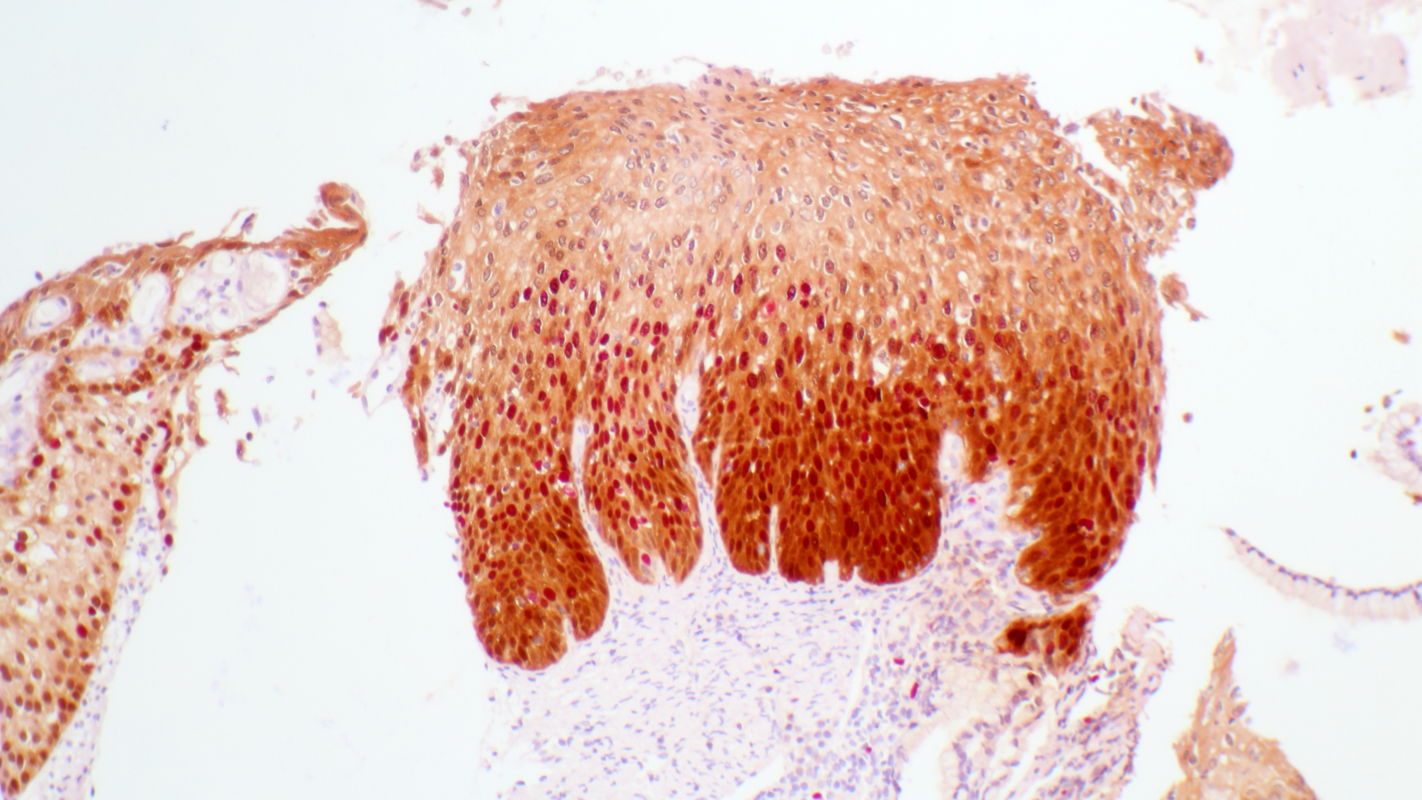
Histopathology of tissue sampled by punch biopsy from the opaque acetowhite lesion at 6 o’clock shows atypical cells that express high concentrations of Ki67 marker into the middle third of the epithelium and of p16 marker into the upper third of the epithelium. The stromal papillae and rete pegs are clearly visible with reflect histologically the colposcopic phenomenon ‘mosaic’. Diagnosis is grade 2 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN 2).
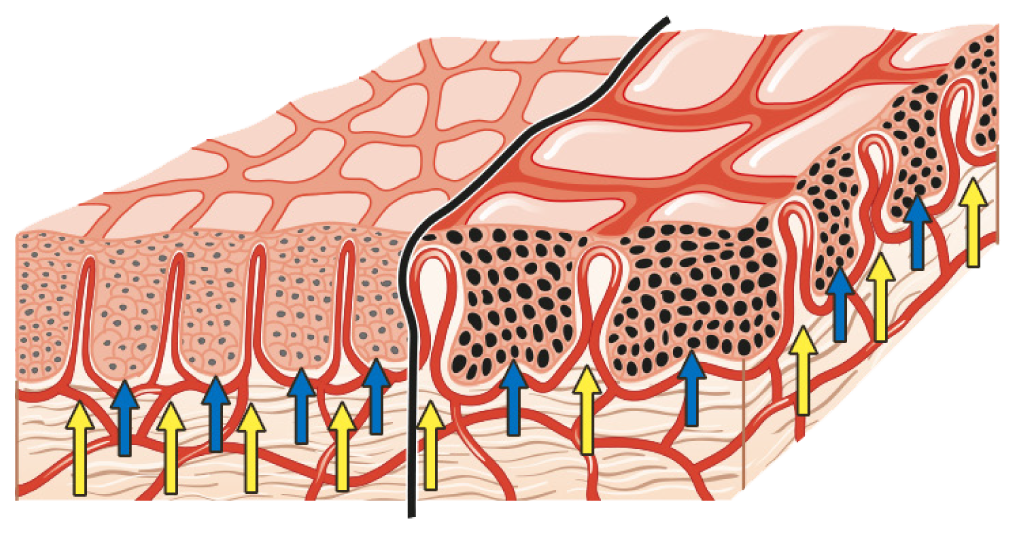
The diagram shows the morphologic basis for the colposcopic finding of mosaic. The stromal papillae (yellow arrows) are interposed between the rete pegs (blue arrows) of the epithelium. Inside the stromal papillae, capillary vessels form loops that rise close to the epithelial surface, where they appear as individual lines. When viewed from above, the capillary vessels form a crisscross pattern that colposcopists call ‘mosaic’. HSIL (right) differs from LSIL (left) in that the rete pegs in neoplastic tissue are widened, causing the vessels to be spaced farther apart.
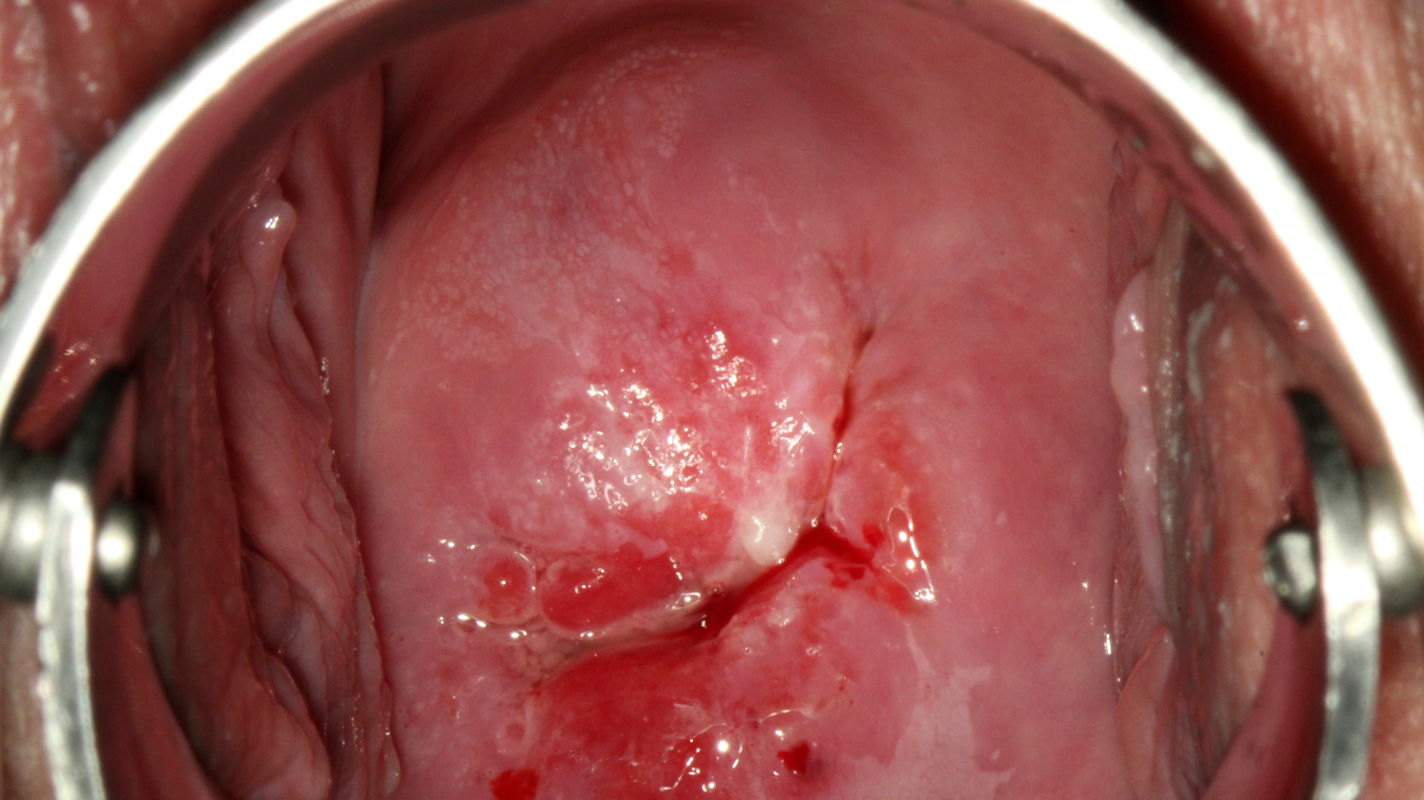
A fine mosaic differs from a coarse mosaic in that the tissue surface is smoother and the vascular lines are spaced closer together. Colposcopic findings in a 29-year-old gravida 1, para 1 with no prior history of disease. The smear was reported as class IIID1, and high risk HPV DNA and RNA were detected.
Colposcopy shows a peripheral acetowhite lesion between 10 and 12 o’clock in an atypical T-zone type 2, which is classified as a normal colposcopic finding.
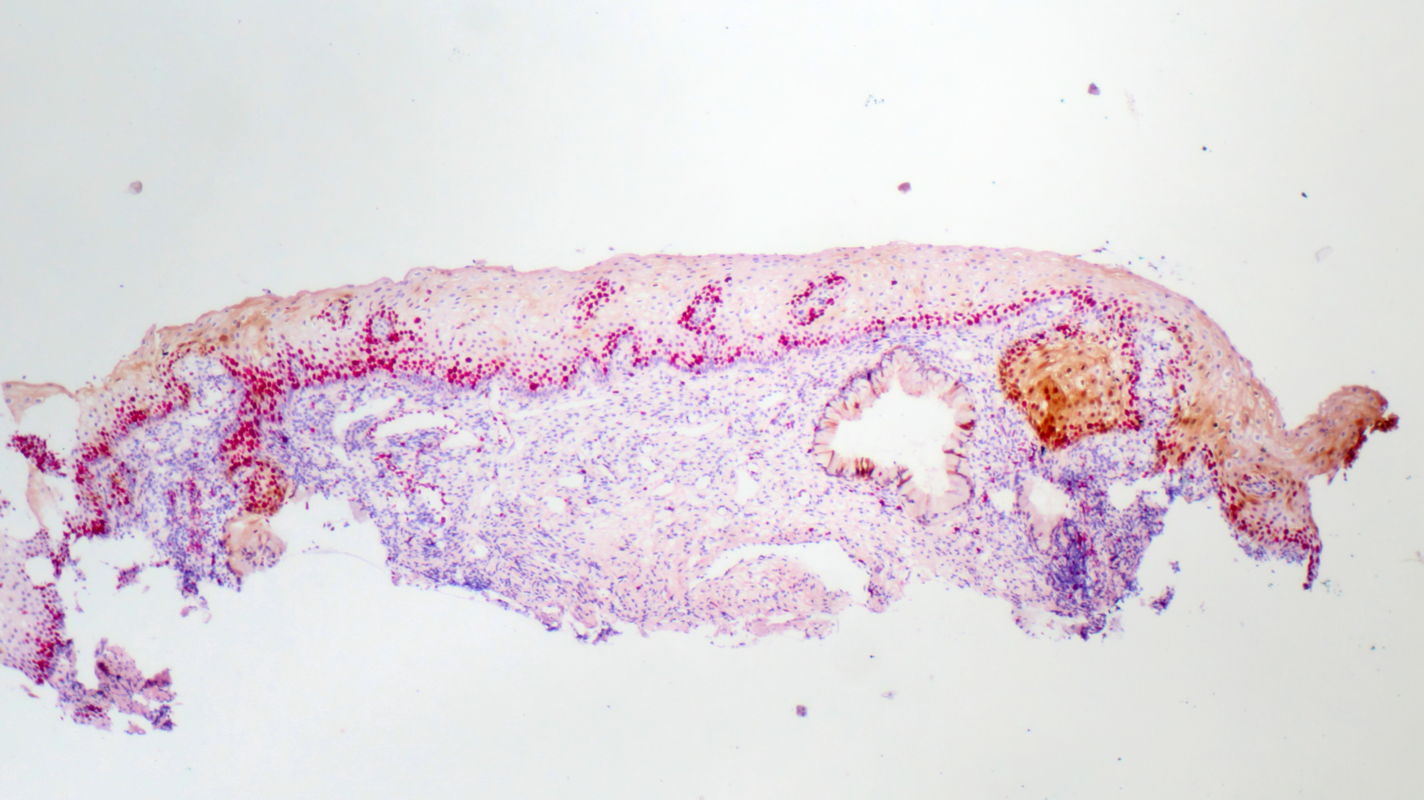
Histopathology of tissue sampled by punch biopsy from the peripheral acetowhite lesion at 11 o’clock shows normally maturing cells that express the marker Ki67 only in the lower third of the epithelium; they are negative for p16. The wide spacing of the stromal papillae is clearly noticeable and reflects the colposcopic phenomenon ‘fine mosaic’. The histologic diagnosis is normal metaplastic epithelium.